


文 章 信 息
负载型金属铱纳米颗粒的碳封装:原位透射电子显微学研究及其对析氢反应的影响
第一作者:刘盼盼(365365最快线路检测中心博士生)
通讯作者:黄兴*
单位:福州大学
文 章 简 介
近日,福州大学黄兴教授课题组在国际知名期刊ACS Nano上发表题为“Carbon Encapsulation of Supported Metallic Iridium Nanoparticles: An in Situ Transmission Electron Microscopy Study and Implications for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction”的研究论文。
该文章采用原位、非原位透射电子显微方法(in situ and ex situ TEM),并结合原位X射线光谱(in situ XPS)和密度泛函理论计算 (DFT calculations)系统研究了碳负载Ir纳米颗粒(NPs)体系中的强金属-载体相互作用(SMSI)的动力学过程、形式机制及其在析氢反应(HER)中的重要作用。作者研究发现,通过对Ir/C材料进行高温加热,可以在Ir纳米颗粒表面诱导形成单层、多层石墨烯(碳)包覆层。该包覆层的形成可有效抑制Ir NPs在高温下的烧结和迁移。此外,电化学测试发现,碳包覆的Ir NPs在电化学析氢反应中明显优于初始(未包覆)Ir/C材料,表现出更好的催化活性和稳定性。
本 文 要 点
要点一:初始Ir/C材料的结构表征
作者通过TEM、XRD等手段对初始Ir/C材料进行了表征。TEM结果显示,Ir NPs在碳载体上分布均匀,尺寸分布为1.5至6.5 nm;HRTEM显示,碳载体具有类似洋葱石墨结构。从选区电子衍射(SAED)可以看出,Ir NPs为金属态,具有面心立方结构。HRTEM表征进一步揭示出初始Ir/C NPs表面干净,无任何碳包覆层。
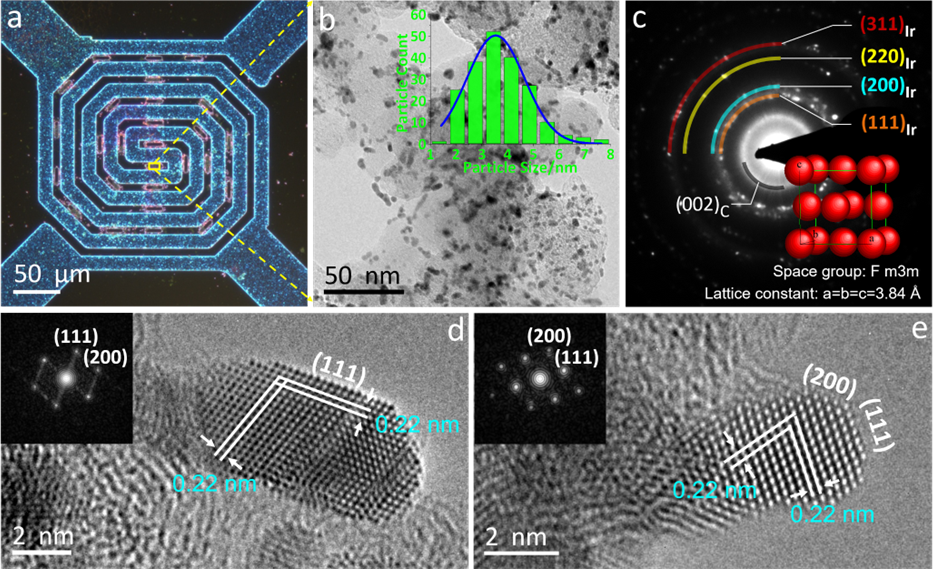
Figure 1. (a) An optical image of a MEMS-based heating chip (SiN film) with the loaded Ir/C specimen. (b) TEM, (c) SAED and (d,e) HRTEM images of Ir/C. Insets in (b), (c) and (d,e) show the particle size distribution, the crystal model of metallic Ir, and the FFT patterns, respectively.
要点二:Ir NPs上碳包覆层的形成以及随温度的变化
原位TEM和XPS结果显示,随着温度的升高(RT to 800℃),强金属-载体相互作用致使在Ir NPs表面诱导形成一层碳包覆层。电子能量损失光谱(EELS)和晶格间距分析证明了该包覆层的碳基成分和结构。值得一提地是,碳包覆层的形成不仅仅限于高真空条件,它也可在氩气或(低压)氢气环境下发生。
此外,利用原位TEM探究了温度变化对包覆层以及界面结构的影响。当温度由800℃降低200°C时,碳覆盖层发生了褶皱变形,这个现象与Ir NPs和碳覆盖层之间的热膨胀系数差异以及金属颗粒表面重构有关。当温度再次升高到800°C时,碳包覆层变得平滑,Ir NPs表面重新形成了清晰的金属-碳包覆层界面。

Figure 2. (a-d, e-h) In situ HRTEM images of Ir/C recorded during the temperature increase from RT to 800 °C. In situ (i) HRTEM, (j) BF-STEM, and (k) SE-STEM images of Ir/C recorded at 800 °C showing the formation of a carbon overlayer on Ir NPs (green arrows). Inset in (i) shows the lattice d-spacing (0.34 nm) of the overlayer. Inset in (j) shows EELS spectra recorded from the overlayer and from the carbon support (red and blue traces, respectively), evidencing that the encapsulated layer is carbon
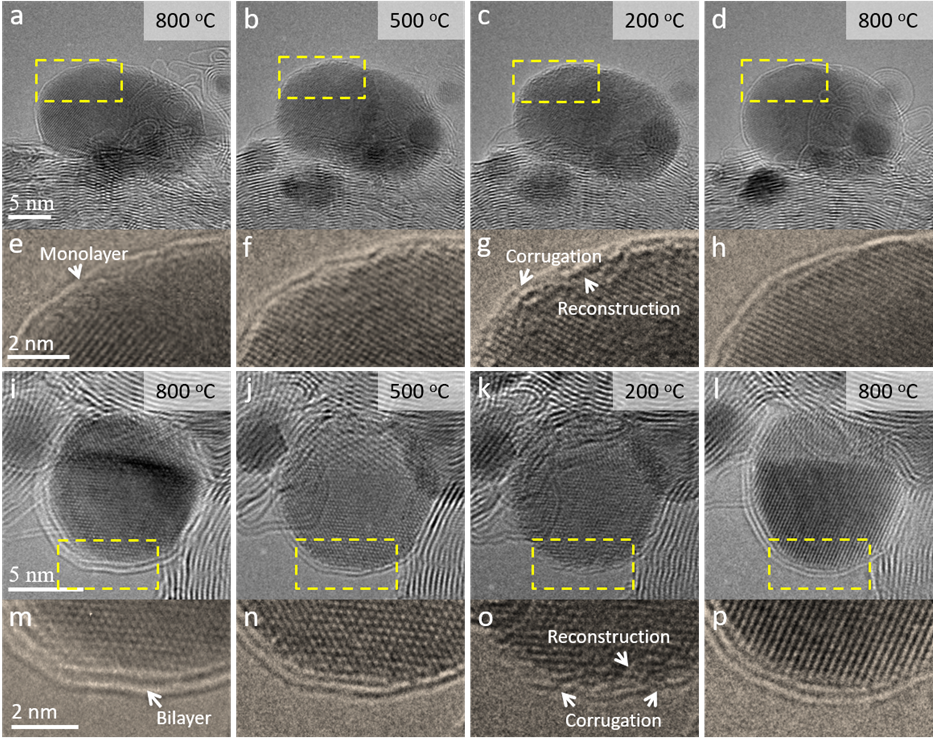
Figure 3. In situ atomic-scale observation of the change of the overlayer and interfacial structure during temperature decrease from 800 °C to 500 °C, and 200 °C and finally increase to 800 °C. (a-d) A monolayer carbon-covered particle. (e-h) Enlarged images within dotted rectangles indicated in (a-d). (i-l) A bilayer carbon-covered particle. (m-p) Enlarged images within dotted rectangles indicated in (i-l).
要点三:封装NPs在高温下的热稳定性及Ir NPs上碳包覆层形成的理论研究
在800°C高温下,通过原位TEM持续跟踪发现,颗粒尺寸没有明显变化。这是由于碳包覆层限制了Ir NPs在碳载体表面的迁移以及奥斯瓦尔德熟化,从而有效抑制了尺寸的增长。
使用密度泛函理论计算(DFT)讨论了在Ir/C中形成碳包覆层的可能原因。理论计算显示,碳原子在Ir(111)表面的吸附能为负值,表明碳包覆层的形成是热力学驱动的。进一步计算结果发现,单层、双层和三层碳包覆情况下,碳原子吸附能(绝对值)逐渐下降,这也解释了为什么大多数包覆的Ir NPs为单层包覆结构。
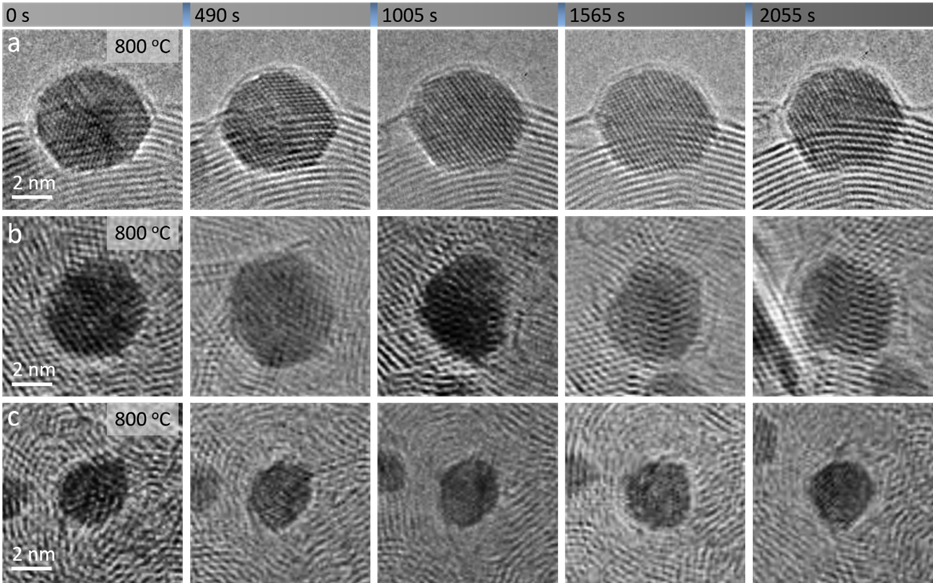
Figure 4. (a-c) Sequential HRTEM images of Ir NPs with different sizes recorded at 800 °C, showing high thermal stability against sintering and migration at 800 °C.
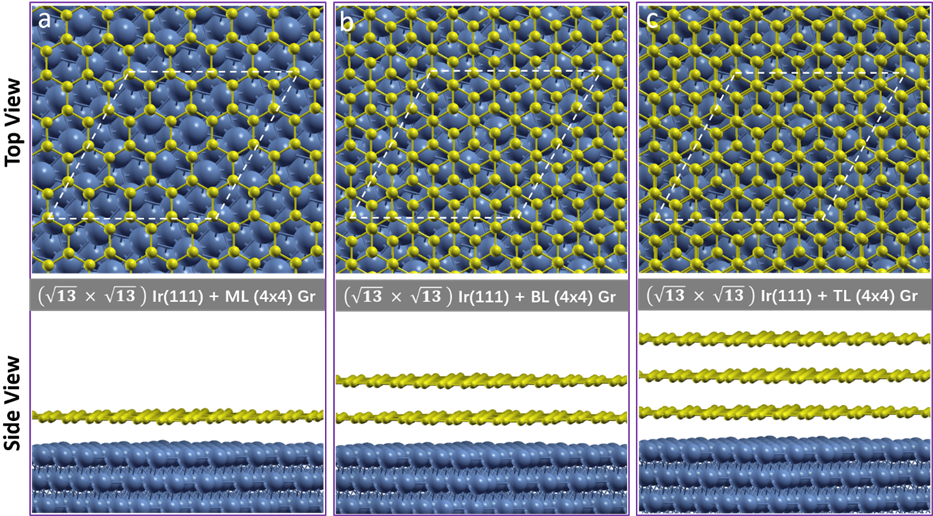
Figure 5. Top view and cross-section view of the structural models of (a) monolayer (b) bilayer (c) trilayer graphene (Gr) on Ir(111). Blue spheres represent Ir atoms and yellow spheres represent C atoms. Unit cell used for the calculations are marked with white dashed lines.
要点四:碳包覆层对催化性能的影响
最后,通过电化学测试探究了碳包覆层对Ir/C析氢性能的影响。结果显示,碳包覆层能够显著提高Ir/C在HER中的催化活性和稳定性。线性扫描伏安法(LSV)测量发现,经过550°C热处理的Ir/C催化剂表现出更高的电流密度。从循环伏安法(CV)和电化学阻抗谱(EIS)结果显示,经过550°C热处理的Ir/C催化剂具有更高的双层电容(更大的活性表面积)和更快的电子传输速率。此外,Tafel斜率结果显示,Ir/C 550°C电极Tafel斜率最低,表明其具有最快的反应动力学和最好的催化活性。多次稳定性测试结果显示,经过550°C和800°C处理的Ir/C比未处理的Ir/C电极表现出更好的稳定性。通过对反应后的催化剂进行HRTEM表征发现,Ir NPs表面的碳包覆层依然稳定存在,并且颗粒尺寸几乎没有明显变化。相反,未经处理的Ir/C颗粒尺度在反应后增长明显。因此,根据实验对比结果可以得出,包覆的催化剂可有效的抑制反应过程中颗粒的团聚,从而提高了催化性能的稳定性。另一方面,金属与碳包覆层之间可能存在电荷转移,产生某种电子结构调制效应,提高了催化剂的活性。总之,通过SMSI在金属颗粒表面诱导形成碳包覆层被证明是一种有效改善碳载金属催化剂性能的手段。
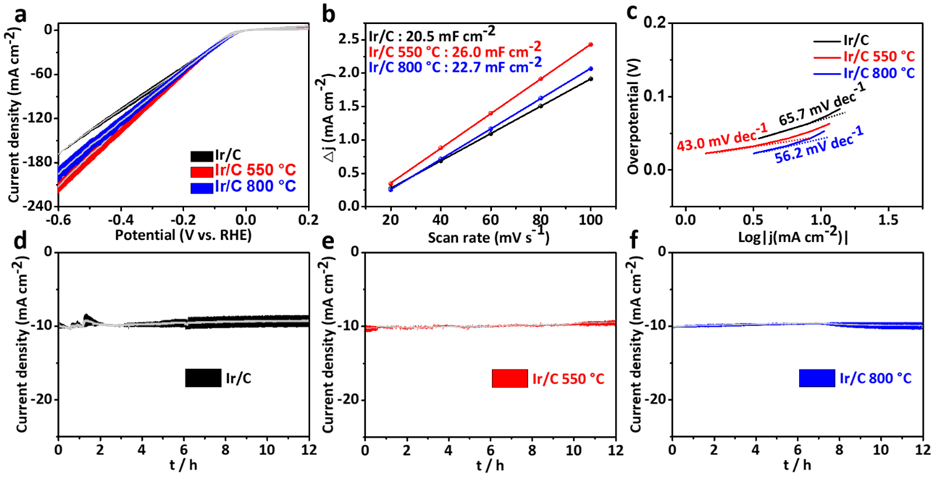
Figure 6. (a) Linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) curves of Ir/C, Ir/C 550 °C and Ir/C 800 °C electrodes in 1 M KOH. Traces represent the standard deviation from three independent measurements. (b) Capacitive currents as a function of scan rates. (c) Tafel plots of the corresponding electrodes (d-f) Current–time curves of Ir/C, Ir/C 550 °C and Ir/C 800 °C electrodes. Traces represent the standard deviation from two independent measurements.
文 章 链 接
Carbon Encapsulation of Supported Metallic Iridium Nanoparticles: An in Situ Transmission Electron Microscopy Study and Implications for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.3c10850
通 讯 作 者 简 介
黄兴教授简介:福建“闽江学者”特聘教授、国家级高层次青年人才。2013年博士毕业于中科院理化技术研究所,先后在德国马普学会弗里茨-哈勃研究所、化学能源转换所、瑞士苏黎世联邦理工学院从事科研工作,2020年加入福州大学,任独立PI;主要从事(原位)电镜在催化、材料领域的应用研究工作(表界面结构、构效机制研究)。在Science, Nat. Catal.,Nature Commun., Adv. Mater., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., Adv. Funct. Mater., ACS Nano, Nano Lett. 等著名学术期刊上发表论文100余篇,引用近8000次,H因子44。